- Latest Pattern Mock Tests including comprehension based questions
- Previous Question Papers with Answer Keys - From 2004 till the most recent exam
- 75 Full Length Mock Tests - New Pattern Paper II, with 100 questions each
- 50 Mini Practice Mock tests - with 25 questions each
- Unlimited Practice - New Questions in every attempt of all mocks
- Questions & Answer Choices randomly shuffled in every attempt for better practice
- Database of over 11000+ MCQs covering the entire syllabus
- Unlimited access and practice for one year from the date of purchase
- Accessible 24 x 7 via Smart-Phone browsers and Desktops
Authentic Feedback from previous LawMint users :
I got AIR 21 in CLAT PG. Thank you so much. Your mocks helped me a lot in my preparation 🙂 - Ayushi Jain
I have subscribed to your CLAT PG program and got AIR 36 in this year CLAT PG. I have also secured AIR 54 in AILET PG exam. I would like to thank you. Your mock paper really helps a lot - Shrashank Tripathi
I would like to thank you for the CLAT PG LLM COURSE. Practising mock tests there helped me in getting confidence and hence I was able to get AIR 45 in CLAT PG LLM - Akshay Awasthi
A year back, I relied on the IIT Kharagpur RGSOIPL mock test series by LawMint to prepare for my RGSOIPL entrance test. Few months back, I relied on your UGC NET Law series to prepare for UGC NET. I was the topper of the RGSOIPL entrance, and have cracked JRF in UGC NET. All thanks to LawMint - Anshuman Sahoo
"I got AIR 18 in CLAT PG and General Category rank 28 in AILET PG. I want to thank you for helping me practice well in controlled conditions from any place. It gave me a lot of confidence and I took the tests while travelling too. I also made it to IIT Kharagpur." - Vinodharani
"Lawmint has been of great help to me in securing AIR 25 in AILET PG and AIR 29 in CLAT PG examinations. The subjective and objective approach of the test series kept me up to date with the latest exam pattern." - Bhawna Nanda
"I, Nimmy Saira Zachariah joined you clat test series. I cleared AILET PG with 30th rank. Your test series were of immense help as it gave me clear idea of where my preparations stand thank you once again law mint." - Nimmy S Z
"Hey guys. Where do I start? If I thought that getting AIR 59 in Clat PG was it, then how wrong I was. With Lawmint now I have cracked UGC NET as well." - Joyanta Chakraborty
Note : Answer Keys to all Previous Question Papers published on LawMint are available to registered users of LawMint.com Online Practice Packs.
Check out all the HECI NTA NET or UGC CBSE NET Paper 1 previous question papers here : Previous Papers & Mock Tests
Note : UGC has rolled out a revised syllabus for both Papers 1 & 2 from Jan 2019 onward.
1. The teacher has been glorified by the phrase “Friend, philosopher and guide” because:
– He has to play all vital roles in the context of society
– He transmits the high value of humanity to students
– He is the great reformer of the society
– He is a great patriot
2. The most important cause of failure for teacher lies in the area of:
– inter personal relationship
– lack of command over the knowledge of the subject
– verbal ability
– strict handling of the students
3. A teacher can establish rapport with his students by:
– becoming a figure of authority
– impressing students with knowledge and skill
– playing the role of a guide
– becoming a friend to the students
4. Education is a powerful instrument of:
– Social transformation
– Personal transformation
– Cultural transformation
– All of the given choices
5. A teacher’s major contribution towards the maximum self-realization of the student is affected through:
– Constant fulfilment of the students’ needs
– Strict control of class-room activities
– Sensitivity to students’ needs, goals and purposes
– Strict reinforcement of academic standards
6. Research problem is selected from the stand point of:
– Researcher’s interest
– Financial support
– Social relevance
– Availability of relevant literature
7. Which one is called non-probability sampling?
– Cluster sampling
– Quota sampling
– Systematic sampling
– Stratified random sampling
8. Formulation of hypothesis may NOT be required in:
– Survey method
– Historical studies
– Experimental studies
– Normative studies
9. Field-work based research is classified as:
– Empirical
– Historical
– Experimental
– Biographical
10. Which of the following sampling method is appropriate to study the prevalence of AIDS amongst male and female in India in 1976, 1986, 1996 and 2006?
– Cluster sampling
– Systematic sampling
– Quota sampling
– Stratified random sampling
11. Read the following passage and answer the question :
The fundamental principle is that Article 14 forbids class legislation but permits reasonable classification for the purpose of legislation which classification must satisfy the twin tests of classification being founded on an intelligible differentia which distinguishes persons or things that are grouped together from those that are left out of the group and that differentia must have a rational nexus to the object sought to be achieved by the Statute in question. The thrust of Article 14 is that the citizen is entitled to equality before law and equal protection of laws. In the very nature of things the society being composed of unequals a welfare State will have to strive by both executive and legislative action to help the less fortunate in society to ameliorate their condition so that the social and economic inequality in the society may be bridged. This would necessitate a legislative application to a group of citizens otherwise unequal and amelioration of whose lot is the object of state affirmative action. In the absence of the doctrine of classification such legislation is likely to flounder on the bed rock of equality enshrined in Article 14. The Court realistically appraising the social and economic inequality and keeping in view the guidelines on which the State action must move as constitutionally laid down in Part IV of the Constitution evolved the doctrine of classification. The doctrine was evolved to sustain a legislation or State action designed to help weaker sections of the society or some such segments of the society in need of succour. Legislative and executive action may accordingly be sustained if it satisfies the twin tests of reasonable classification and the rational principle correlated to the object sought to be achieved.
The concept of equality before the law does not involve the idea of absolute equality among human beings which is a physical impossibility. All that Article 14 guarantees is a similarity of treatment contra-distinguished from identical treatment. Equality before law means that among equals the law should be equal and should be equally administered and that the likes should be treated alike. Equality before the law does not mean that things which are different shall be as though they are the same. It of course means denial of any special privilege by reason of birth, creed or the like. The legislation as well as the executive government, while dealing with diverse problems arising out of an infinite variety of human relations must of necessity have the power of making special laws, to attain any particular object and to achieve that object it must have the power of selection or classification of persons and things upon which such laws are to operate.
Right to equality, one of the fundamental rights, is enunciated in the constitution under Part III, Article:
(A)12
– 13
– 14
– 15
12. Read the following passage and answer the question :
The fundamental principle is that Article 14 forbids class legislation but permits reasonable classification for the purpose of legislation which classification must satisfy the twin tests of classification being founded on an intelligible differentia which distinguishes persons or things that are grouped together from those that are left out of the group and that differentia must have a rational nexus to the object sought to be achieved by the Statute in question. The thrust of Article 14 is that the citizen is entitled to equality before law and equal protection of laws. In the very nature of things the society being composed of unequals a welfare State will have to strive by both executive and legislative action to help the less fortunate in society to ameliorate their condition so that the social and economic inequality in the society may be bridged. This would necessitate a legislative application to a group of citizens otherwise unequal and amelioration of whose lot is the object of state affirmative action. In the absence of the doctrine of classification such legislation is likely to flounder on the bed rock of equality enshrined in Article 14. The Court realistically appraising the social and economic inequality and keeping in view the guidelines on which the State action must move as constitutionally laid down in Part IV of the Constitution evolved the doctrine of classification. The doctrine was evolved to sustain a legislation or State action designed to help weaker sections of the society or some such segments of the society in need of succour. Legislative and executive action may accordingly be sustained if it satisfies the twin tests of reasonable classification and the rational principle correlated to the object sought to be achieved.
The concept of equality before the law does not involve the idea of absolute equality among human beings which is a physical impossibility. All that Article 14 guarantees is a similarity of treatment contra-distinguished from identical treatment. Equality before law means that among equals the law should be equal and should be equally administered and that the likes should be treated alike. Equality before the law does not mean that things which are different shall be as though they are the same. It of course means denial of any special privilege by reason of birth, creed or the like. The legislation as well as the executive government, while dealing with diverse problems arising out of an infinite variety of human relations must of necessity have the power of making special laws, to attain any particular object and to achieve that object it must have the power of selection or classification of persons and things upon which such laws are to operate.
The main thrust of Right to equality is that it permits:
– class legislation
– equality before law and equal protection under the law
– absolute equality
– special privilege by reason of birth
13. Read the following passage and answer the question :
The fundamental principle is that Article 14 forbids class legislation but permits reasonable classification for the purpose of legislation which classification must satisfy the twin tests of classification being founded on an intelligible differentia which distinguishes persons or things that are grouped together from those that are left out of the group and that differentia must have a rational nexus to the object sought to be achieved by the Statute in question. The thrust of Article 14 is that the citizen is entitled to equality before law and equal protection of laws. In the very nature of things the society being composed of unequals a welfare State will have to strive by both executive and legislative action to help the less fortunate in society to ameliorate their condition so that the social and economic inequality in the society may be bridged. This would necessitate a legislative application to a group of citizens otherwise unequal and amelioration of whose lot is the object of state affirmative action. In the absence of the doctrine of classification such legislation is likely to flounder on the bed rock of equality enshrined in Article 14. The Court realistically appraising the social and economic inequality and keeping in view the guidelines on which the State action must move as constitutionally laid down in Part IV of the Constitution evolved the doctrine of classification. The doctrine was evolved to sustain a legislation or State action designed to help weaker sections of the society or some such segments of the society in need of succour. Legislative and executive action may accordingly be sustained if it satisfies the twin tests of reasonable classification and the rational principle correlated to the object sought to be achieved.
The concept of equality before the law does not involve the idea of absolute equality among human beings which is a physical impossibility. All that Article 14 guarantees is a similarity of treatment contra-distinguished from identical treatment. Equality before law means that among equals the law should be equal and should be equally administered and that the likes should be treated alike. Equality before the law does not mean that things which are different shall be as though they are the same. It of course means denial of any special privilege by reason of birth, creed or the like. The legislation as well as the executive government, while dealing with diverse problems arising out of an infinite variety of human relations must of necessity have the power of making special laws, to attain any particular object and to achieve that object it must have the power of selection or classification of persons and things upon which such laws are to operate.
The social and economic inequality in the society can be bridged by:
– executive and legislative action
– universal suffrage
– identical treatment
– none of the above
14. Read the following passage and answer the question :
The fundamental principle is that Article 14 forbids class legislation but permits reasonable classification for the purpose of legislation which classification must satisfy the twin tests of classification being founded on an intelligible differentia which distinguishes persons or things that are grouped together from those that are left out of the group and that differentia must have a rational nexus to the object sought to be achieved by the Statute in question. The thrust of Article 14 is that the citizen is entitled to equality before law and equal protection of laws. In the very nature of things the society being composed of unequals a welfare State will have to strive by both executive and legislative action to help the less fortunate in society to ameliorate their condition so that the social and economic inequality in the society may be bridged. This would necessitate a legislative application to a group of citizens otherwise unequal and amelioration of whose lot is the object of state affirmative action. In the absence of the doctrine of classification such legislation is likely to flounder on the bed rock of equality enshrined in Article 14. The Court realistically appraising the social and economic inequality and keeping in view the guidelines on which the State action must move as constitutionally laid down in Part IV of the Constitution evolved the doctrine of classification. The doctrine was evolved to sustain a legislation or State action designed to help weaker sections of the society or some such segments of the society in need of succour. Legislative and executive action may accordingly be sustained if it satisfies the twin tests of reasonable classification and the rational principle correlated to the object sought to be achieved.
The concept of equality before the law does not involve the idea of absolute equality among human beings which is a physical impossibility. All that Article 14 guarantees is a similarity of treatment contra-distinguished from identical treatment. Equality before law means that among equals the law should be equal and should be equally administered and that the likes should be treated alike. Equality before the law does not mean that things which are different shall be as though they are the same. It of course means denial of any special privilege by reason of birth, creed or the like. The legislation as well as the executive government, while dealing with diverse problems arising out of an infinite variety of human relations must of necessity have the power of making special laws, to attain any particular object and to achieve that object it must have the power of selection or classification of persons and things upon which such laws are to operate.
The doctrine of classification is evolved to:
– Help weaker sections of the society
– Provide absolute equality
– Provide identical treatment
– None of the given choices
15. Read the following passage and answer the question :
The fundamental principle is that Article 14 forbids class legislation but permits reasonable classification for the purpose of legislation which classification must satisfy the twin tests of classification being founded on an intelligible differentia which distinguishes persons or things that are grouped together from those that are left out of the group and that differentia must have a rational nexus to the object sought to be achieved by the Statute in question. The thrust of Article 14 is that the citizen is entitled to equality before law and equal protection of laws. In the very nature of things the society being composed of unequals a welfare State will have to strive by both executive and legislative action to help the less fortunate in society to ameliorate their condition so that the social and economic inequality in the society may be bridged. This would necessitate a legislative application to a group of citizens otherwise unequal and amelioration of whose lot is the object of state affirmative action. In the absence of the doctrine of classification such legislation is likely to flounder on the bed rock of equality enshrined in Article 14. The Court realistically appraising the social and economic inequality and keeping in view the guidelines on which the State action must move as constitutionally laid down in Part IV of the Constitution evolved the doctrine of classification. The doctrine was evolved to sustain a legislation or State action designed to help weaker sections of the society or some such segments of the society in need of succour. Legislative and executive action may accordingly be sustained if it satisfies the twin tests of reasonable classification and the rational principle correlated to the object sought to be achieved.
The concept of equality before the law does not involve the idea of absolute equality among human beings which is a physical impossibility. All that Article 14 guarantees is a similarity of treatment contra-distinguished from identical treatment. Equality before law means that among equals the law should be equal and should be equally administered and that the likes should be treated alike. Equality before the law does not mean that things which are different shall be as though they are the same. It of course means denial of any special privilege by reason of birth, creed or the like. The legislation as well as the executive government, while dealing with diverse problems arising out of an infinite variety of human relations must of necessity have the power of making special laws, to attain any particular object and to achieve that object it must have the power of selection or classification of persons and things upon which such laws are to operate.
While dealing with diverse problems arising out of an infinite variety of human relations, the government
– must have the power of making special laws
– must not have any power to make special laws
– must have power to withdraw equal rights
– none of the above
16. Communication with oneself is known as:
– Group communication
– Grapevine communication
– Interpersonal communication
– Intrapersonal communication
17. Which broadcasting system for TV is followed in India?
– NTSE
– PAL
– SECAM
– NTCS
18. All India Radio before 1936 was known as:
– Indian Radio Broadcasting
– Broadcasting Service of India
– Indian Broadcasting Service
– All India Broadcasting Service
19. The biggest news agency of India is:
– PTI
– UNI
– NANAP
– Samachar Bharati
20. Prasar Bharati was launched in the year:
– 1995
– 1997
– 1999
– 2001
21. A statistical measure based upon the entire population is called parameter while measure based upon a sample is known as:
– Sample parameter
– Inference
– Statistics
– None of the given choices
22. The importance of the correlation co-efficient lies in the fact that:
– There is a linear relationship between the correlated variables.
– It is one of the most valid measure of statistics.
– It allows one to determine the degree or strength of the association between two variables.
– It is a non-parametric method of statistical analysis.
23. The F-test:
– is essentially a two tailed test.
– is essentially a one tailed test.
– can be one tailed as well as two tailed depending on the hypothesis.
– can never be a one tailed test.
24. What will be the next letter in the following series? DCXW, FGVU, HGTS
– AKPO
– JBYZ
– JIRQ
– LMRS
25. The following question is based on the diagram given below. If the two small circles represent formal class-room education and distance education and the big circle stands for university system of education, which figure represents the university systems?
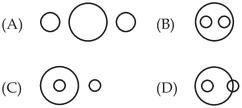
– A
– B
– C
– D
26. The statement, ‘To be non-violent is good’ is a:
– Moral judgement
– Factual judgement
– Religious judgement
– Value judgement
27. Assertion (A): Man is a rational being.
Reason (R): Man is a social being.
– Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
– Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
– (A) is true but (R) is false
– (A) is false but (R) is true
28. Value Judgements are:
– Factual Judgements
– Ordinary Judgements
– Normative Judgements
– Expression of public opinion
29. Deductive reasoning proceeds from:
– general to particular
– particular to general
– one general conclusion to another general conclusion
– one particular conclusion to another particular conclusion
30. AGARTALA is written in code as 14168171, the code for AGRA is:
– 1641
– 1416
– 1441
– 1461
31. Which one of the following is the most comprehensive source of population data?
– National Family Health Surveys
– National Sample Surveys
– Census
– Demographic Health Surveys
32. Which one of the following principles is not applicable to sampling?
– Sample units must be clearly defined
– Sample units must be dependent on each other
– Same units of sample should be used throughout the study
– Sample units must be chosen in a systematic and objective manner
33. If January 1st, 2007 is Monday, what was the day on 1st January 1995?
– Sunday
– Monday
– Friday
– Saturday
34. Insert the missing number in the following series:
4 16 8 64 ? 256
– 16
– 24
– 32
– 20
35. If an article is sold for Rs. 178 at a loss of 11%; what would be its selling price in order to earn a profit of 11%?
– Rs. 222.50
– Rs. 267
– Rs. 222
– Rs. 220
36. WYSIWYG – describes the display of a document on screen as it will actually print:
– What you state is what you get
– What you see is what you get
– What you save is what you get
– What you suggest is what you get
37. Which of the following is not a Computer language?
– PASCAL
– UNIX
– FORTRAN
– COBOL
38. A key-board has at least:
– 91 keys
– 101 keys
– 111 keys
– 121 keys
39. An E-mail address is composed of:
– two parts
– three parts
– four parts
– five parts
40. Corel Draw is a popular:
– Illustration programme
– Programming language
– Text programme
– None of the given choices
41. Human ear is most sensitive to noise in which of the following ranges:
– 20 Hz to 20 kHz.
– 100 Hz to 500 Hz
– 10 to 12 KHz
– 13 to 16 KHz
42. Which one of the following units is used to measure intensity of noise?
– decibel
– Hz
– Phon
– Watts/m2
43. If the population growth follows a logistic curve, the maximum sustainable yield:
– is equal to half the carrying capacity.
– is equal to the carrying capacity.
– depends on growth rates.
– depends on the initial population.
44. Chemical weathering of rocks is largely dependent upon:
– high temperature
– strong wind action
– heavy rainfall
– glaciation
45. Structure of earth’s system consists of the following: Match List-I with List-II and give the correct answer.
List-I (Zone)
(a) Atmosphere
(b) Biosphere
(c) Hydrosphere
(d) Lithosphere
(i) Inert gases
(ii) Salt, fresh water, snow and ice
(iii) Organic substances, skeleton matter
(iv) Light silicates
Choose the answer which corresponds to the order : (a) (b) (c) (d)
– (ii) (iii) (i) (iv)
– (i) (iii) (ii) (iv)
– (ii) (i) (iii) (iv)
– (iii) (i) (ii) (iv)
46. NAAC is an autonomous institution under the aegis of:
– ICSSR
– CSIR
– AICTE
– UGC
47. National Council for Women’s Education was established in:
– 1958
– 1976
– 1989
– 2000
48. Which one of the following is not situated in New Delhi?
– Indian Council of Cultural Relations
– Indian Council of Scientific Research
– National Council of Educational Research and Training
– Indian Institute of Advanced Studies
49. Autonomy in higher education implies freedom in:
– Administration
– Policy-making
– Finance
– Curriculum development
50. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer from the code given below:
List-I (Institutions)
(a) Dr. Hari Singh Gour University
(b) S.N.D.T. University
(c) M.S. University
(d) J.N. Vyas University
List-II (Locations)
(i) Mumbai
(ii) Baroda
(iii) Jodhpur
(iv) Sagar
Choose the answer that corresponds to the order : (a) (b) (c) (d)
– (iv) (i) (ii) (iii)
– (i) (ii) (vi) (iv)
– (iii) (i) (ii) (iv)
– (ii) (iv) (i) (iii)
- Latest Pattern Mock Tests including comprehension based questions
- Previous Question Papers with Answer Keys - From 2004 till the most recent exam
- 75 Full Length Mock Tests - New Pattern Paper II, with 100 questions each
- 50 Mini Practice Mock tests - with 25 questions each
- Unlimited Practice - New Questions in every attempt of all mocks
- Questions & Answer Choices randomly shuffled in every attempt for better practice
- Database of over 11000+ MCQs covering the entire syllabus
- Unlimited access and practice for one year from the date of purchase
- Accessible 24 x 7 via Smart-Phone browsers and Desktops
Authentic Feedback from previous LawMint users :
I got AIR 21 in CLAT PG. Thank you so much. Your mocks helped me a lot in my preparation 🙂 - Ayushi Jain
I have subscribed to your CLAT PG program and got AIR 36 in this year CLAT PG. I have also secured AIR 54 in AILET PG exam. I would like to thank you. Your mock paper really helps a lot - Shrashank Tripathi
I would like to thank you for the CLAT PG LLM COURSE. Practising mock tests there helped me in getting confidence and hence I was able to get AIR 45 in CLAT PG LLM - Akshay Awasthi
A year back, I relied on the IIT Kharagpur RGSOIPL mock test series by LawMint to prepare for my RGSOIPL entrance test. Few months back, I relied on your UGC NET Law series to prepare for UGC NET. I was the topper of the RGSOIPL entrance, and have cracked JRF in UGC NET. All thanks to LawMint - Anshuman Sahoo
"I got AIR 18 in CLAT PG and General Category rank 28 in AILET PG. I want to thank you for helping me practice well in controlled conditions from any place. It gave me a lot of confidence and I took the tests while travelling too. I also made it to IIT Kharagpur." - Vinodharani
"Lawmint has been of great help to me in securing AIR 25 in AILET PG and AIR 29 in CLAT PG examinations. The subjective and objective approach of the test series kept me up to date with the latest exam pattern." - Bhawna Nanda
"I, Nimmy Saira Zachariah joined you clat test series. I cleared AILET PG with 30th rank. Your test series were of immense help as it gave me clear idea of where my preparations stand thank you once again law mint." - Nimmy S Z
"Hey guys. Where do I start? If I thought that getting AIR 59 in Clat PG was it, then how wrong I was. With Lawmint now I have cracked UGC NET as well." - Joyanta Chakraborty
Note : Answer Keys to all Previous Question Papers published on LawMint are available to registered users of our Online Practice Packs.
Check out all the HECI NTA NET or UGC CBSE NET Paper 1 previous question papers here : Previous Papers & Mock Tests











